FAQ/ Water Level Calculation Logic for Flowing Flood¶
How do you determine the cell water level in a downflowing flood?
What is the logic?
response¶
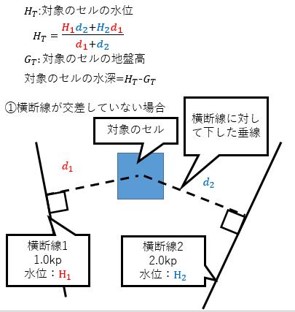
Demonstrates the logic for determining the water level of a flowing flood.
- \(H_1\): Water level at transverse line 1
- \(d_1\): length of the line perpendicular to the transverse line 1 to the center of the target cell
- \(H_2\): Water level at transverse line 2
- \(d_2\): length of the line perpendicular to the cross line 2 to the center of the target cell
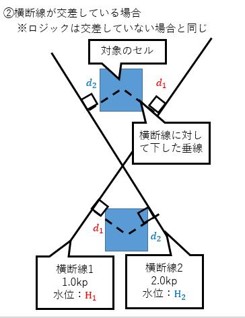
If the transverse lines intersect, the logic is the same.
The "Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism Guidebook for Flood Estimation Maps of Small Rivers (June Reiwa)" has the following request.
Cite !!! "Guide to Flood Estimation Maps of Small Rivers (June Reiwa), p . 24" 6.2 Flowing flooding The water level for each interpolation node is calculated by setting nodes to interpolate between cross-sectional lines at a pitch of 25 m, etc., and interpolating the calculated water level for each cross-sectional survey line in a straight line.
In DioVISTA, you can interpolate between transverse lines at any pitch (for example, 25m pitch) by interpolating transverse lines. The interpolated cross-sectional shape is created by interpolating from the cross-sectional shape of the front and rear sections. The water level in the interpolated cross-section is calculated by unequal flow calculation and irregular flow calculation. The water level of the uninterpolated cross-section is calculated by unequal flow calculation and irregular flow calculation, and it is not the water level interpolated from that water level.